Action Types
AI AgentsIntelligent assistants that can access multiple tools and make decisions. Capabilities:
- Access to multiple integrations simultaneously
- Natural language processing and decision-making
- Context awareness across workflow steps
- Ability to handle complex, multi-step tasks
Direct, programmatic actions for specific tasks. Capabilities:
- Precise, deterministic operations
- Fast execution for simple tasks
- Direct API calls to connected apps
- Structured data processing
Adding Actions to Workflows
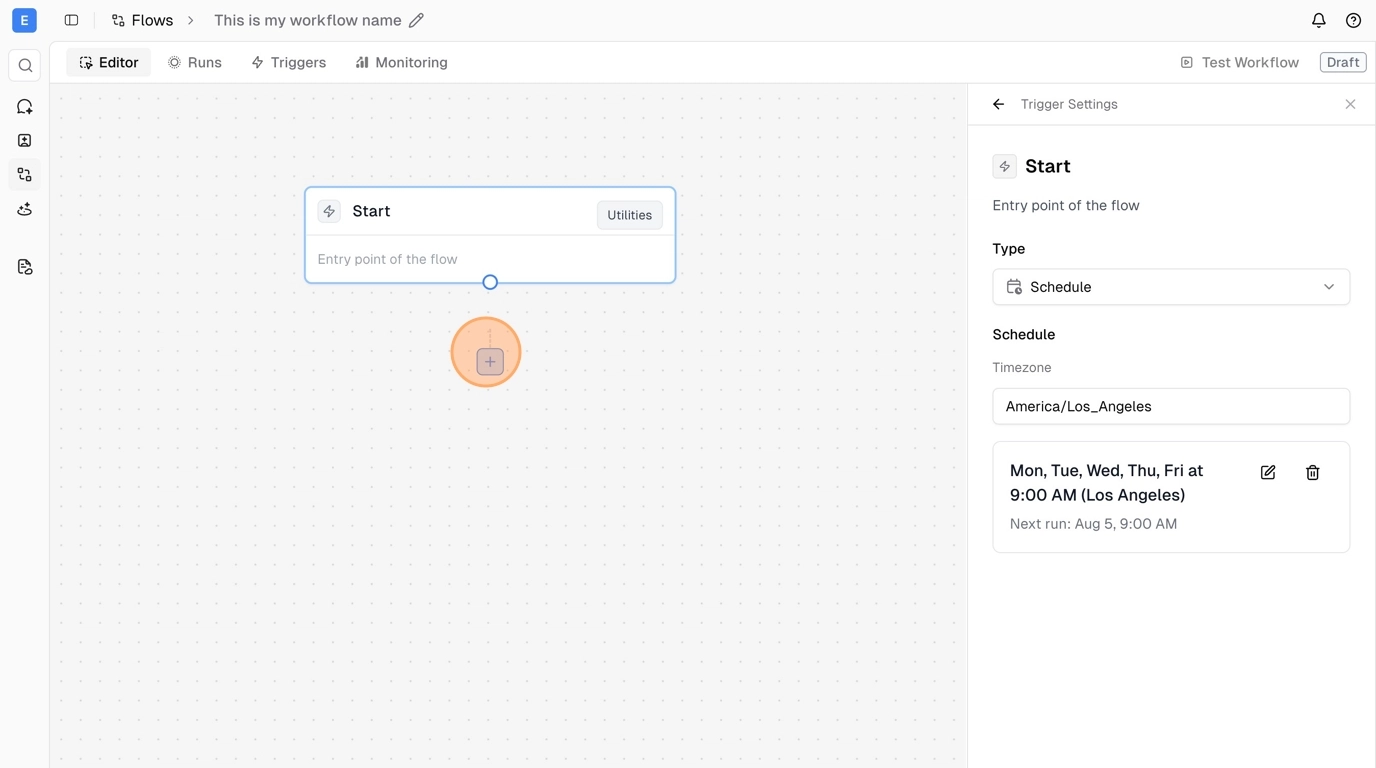
- Click the blue + on any node or use the + in the flow dock
- Choose action type: Agent or Tool
- Configure settings: Select integrations and permissions
- Connect nodes: Link actions in logical sequence
- Add Exit node: Every workflow must end with an Exit node
Configuring AI Agents
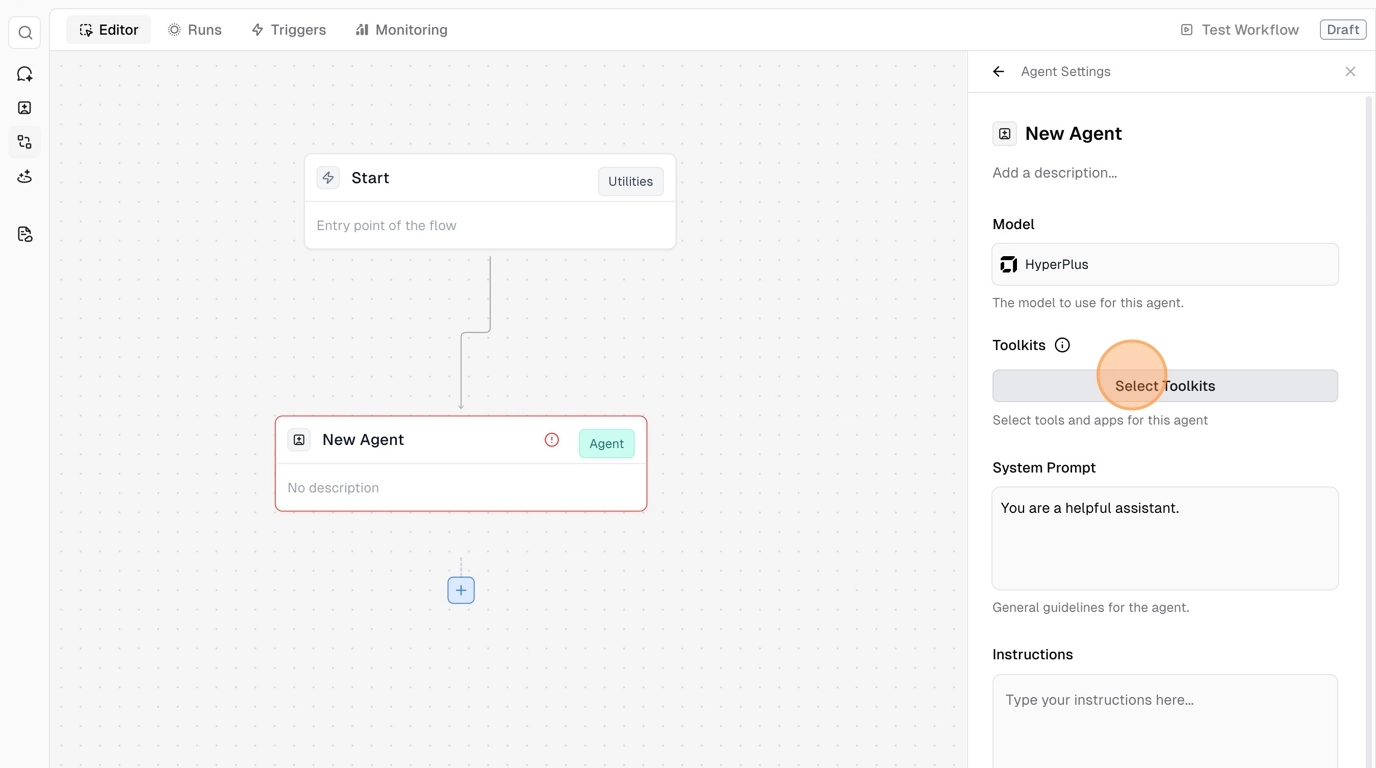
Toolkit Selection
Give your agent access to the tools it needs:- Select Toolkits: Choose integrations like Gmail, HubSpot, Google Sheets
- Choose Connections: Select which specific accounts to use
- Set Permissions: Configure read/write access levels
Approval Requirements
Control sensitive operations by requiring human approval:- Email Sending: Approve outbound messages
- Data Deletion: Confirm destructive operations
- Financial Actions: Verify payment processing
- External Communications: Review customer-facing content
System Instructions
- “Check my Gmail for any emails that require a response, and go ahead and respond for me”
- “Analyze sales data from Google Sheets and create a summary report”
- “Find new leads in HubSpot and send personalized LinkedIn connection requests”
Workflow Architecture
Sequential Actions
Create linear workflows where each action depends on the previous:Parallel Processing
Execute multiple actions simultaneously for efficiency:Conditional Logic
Add decision points based on data or outcomes:Complex Workflow Examples
Lead Processing Pipeline- Apollo Tool: Find new prospects
- Agent: Analyze and qualify leads
- Google Sheets Tool: Add to CRM
- Gmail Agent: Send personalized outreach
- HubSpot Tool: Create follow-up tasks
- Web Search Tool: Find trending topics
- Agent: Generate content ideas
- Image Generation Tool: Create visuals
- LinkedIn Agent: Write and schedule posts
- Analytics Tool: Track performance
- Gmail Tool: Monitor support inbox
- Agent: Categorize and prioritize tickets
- Knowledge Base Tool: Find relevant solutions
- Agent: Draft personalized responses
- CRM Tool: Update customer records
Workflow Completion